Leptin: What It Is And How It Works
Hormones are substances secreted by specialized glands that regulate multiple functions of the body. Leptin is a protein that is formed mainly in the body’s adipose tissue.
It can also be secreted in the liver, placenta, and gastric mucosa. Once released, leptin passes into the blood and acts as a signal to the brain. This hormone is mainly related to intake. When you finish eating, she is in charge of warning the brain that you are already satiated and, consequently, you will lose your appetite.
When you eat abundantly, its levels in the bloodstream remain elevated for longer. The same happens during pregnancy because, as you will see later, it is essential for the development of the baby.
Leptin levels in normal-weight people are around 18 ng / ml, with levels higher in women than in men. When you gain weight you can reach 30 ng / ml.
All about leptin
The control of appetite and satiety is carried out by a brain region called the hypothalamus . In its structure is the arcuate nucleus that is stimulated by leptin and will release chemical substances capable of inhibiting or inducing the sensation of hunger.
For example, when you’ve eaten heavily, leptin reaches the arcuate nucleus. This sends signals to other structures to stop the secretion of neuropeptide Y. This measure will decrease your appetite and increase internal energy expenditure.
When there are genetic defects that involve the lack of this hormone, people tend to suffer from morbid obesity from an early age.
Leptin levels are related to insulin levels. The insulin is a hormone released by the pancreas to increase the sugar content in blood, for example, after the meal.
Its secretion helps glucose from food to pass from the blood to the tissues. Leptin has been observed to inhibit insulin secretion and activate the use of fat for energy.
Other functions of leptin
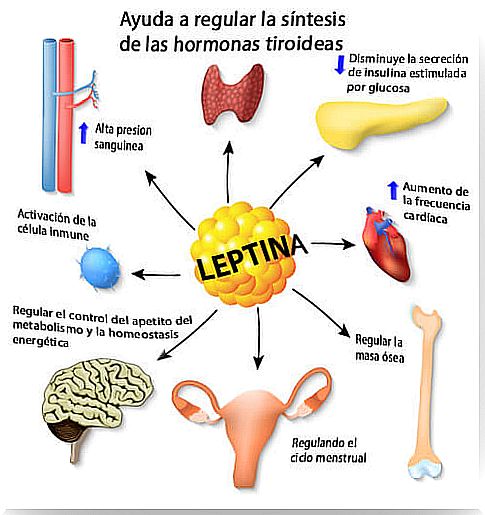
Although the best known function is the regulation of the amount of adipose tissue and appetite, this hormone is involved in many other metabolic processes.
Supports angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels from existing ones. It is a normal phenomenon during embryonic development, growth and tissue healing. It appears that leptin stimulates angiogenesis by stimulating cell division.
Onset of puberty and reproductive functions
It has recently been observed that the increase in body fat that women experience at the beginning of puberty is indicated by a similar concentration of leptin.
In addition, leptin stimulates the synthesis of gonadal steroids that initiate the development of the reproductive system. Some scientists propose to use this hormone as an indicator of the onset of pubertal development.
Intervenes in fetal development
During pregnancy, this hormone is produced in the placenta; its values increase in maternal blood, especially in the second trimester, and decrease after delivery.
Some research suggests that leptin may act as a growth factor during pregnancy. It could also indicate an adequate supply of nutrients from the mother to the fetus.
Collaborates with the immune system
Leptin activates the cells of the immune system and promotes inflammation. That way, the virus or bacteria that is attacking the body will be eliminated more quickly.
Leptin: a hormone with many functions
Leptin regulates energy homeostasis, neuroendocrine function, and metabolism. Deficiency of this hormone is a clinical syndrome associated with obesity, hypothalamic amenorrhea, and lipoatrophy.
Obese people often develop resistance to leptin. Your levels are high, but your brain can’t recognize the hormone’s signal to stop eating. Most leptin supplements do not contain the hormone, but rather a mixture of nutrients that can improve leptin sensitivity.
However, research is lacking to demonstrate its effectiveness for weight loss. Making positive diet and lifestyle changes is a much more effective way to improve leptin sensitivity and promote weight loss.