Acoustic Trauma: Symptoms And Treatments
It is important to know that acoustic trauma causes decrease or loss of hearing. Therefore, it is best to prevent it from happening, since it is currently a treatable but incurable condition.

Acoustic trauma is a form of deafness caused by the impact of very loud sounds. These damage the internal auditory system and affect hearing, either temporarily or permanently.
Sound is a physical phenomenon that propagates through waves made up of vibrating molecules. Therefore, the impact of a loud sound is not only perceptual, but also physical and can lead to acoustic trauma.
Not everyone is aware of the effect that a very intense sound can have. Using headphones at a very high volume for prolonged periods can cause hearing damage. One of them is acoustic trauma.
What is an acoustic trauma?

In a strict sense, an acoustic trauma is an injury to the inner ear. It can be caused by a single exposure to very loud noise, such as a gunshot or explosion, or by continuous exposure to loud noise.
It is estimated that anyone who is exposed to noise of 85 decibels or more continuously and without protection can suffer acoustic trauma. On some occasions, this injury can also be the result of a blow to the head.
Acoustic trauma leads to damage to the mechanism by which vibrations are processed within the ear. This, in turn, results in hearing loss. It has various levels of severity, depending on the severity of the injury.
Causes of acoustic trauma
There are two causes of acoustic trauma, as already noted. One is exposure to extremely loud noise on a single occasion. The other, a continuous exposure to loud noises. A safe hearing environment is considered to be one that does not exceed 70 decibels.
The three factors that influence the severity of acoustic trauma are:
- The intensity of the sound.
- The frequency or pitch of the sound: the louder, the more damaging.
- The total exposure time.
Some people are more exposed to this type of auditory stimuli. Those who work with noisy industrial equipment or in an environment with a lot of noise pollution are at higher risk of hearing trauma. Also those who listen to music at high volumes or practice shooting, for example.
Symptoms of acoustic trauma
The main symptom of this type of trauma is hearing loss. In the most severe cases, no sound is perceived. If the injury is not that severe, you may have difficulty picking up low-frequency sounds. Also, there may be a distortion in the perception of high-frequency sounds.
There are also times when a major symptom known as tinnitus occurs. In these cases, the injury leads to buzzing, whistling or ringing sounds, without these coming from an external source.
If the tinnitus is mild or moderate, those buzzes or whistles will only be heard when the person is in a quiet environment. If it is more severe or chronic, they are perceived in any type of environment. This last scenario is the most common in acoustic trauma.
Diagnosis and treatment
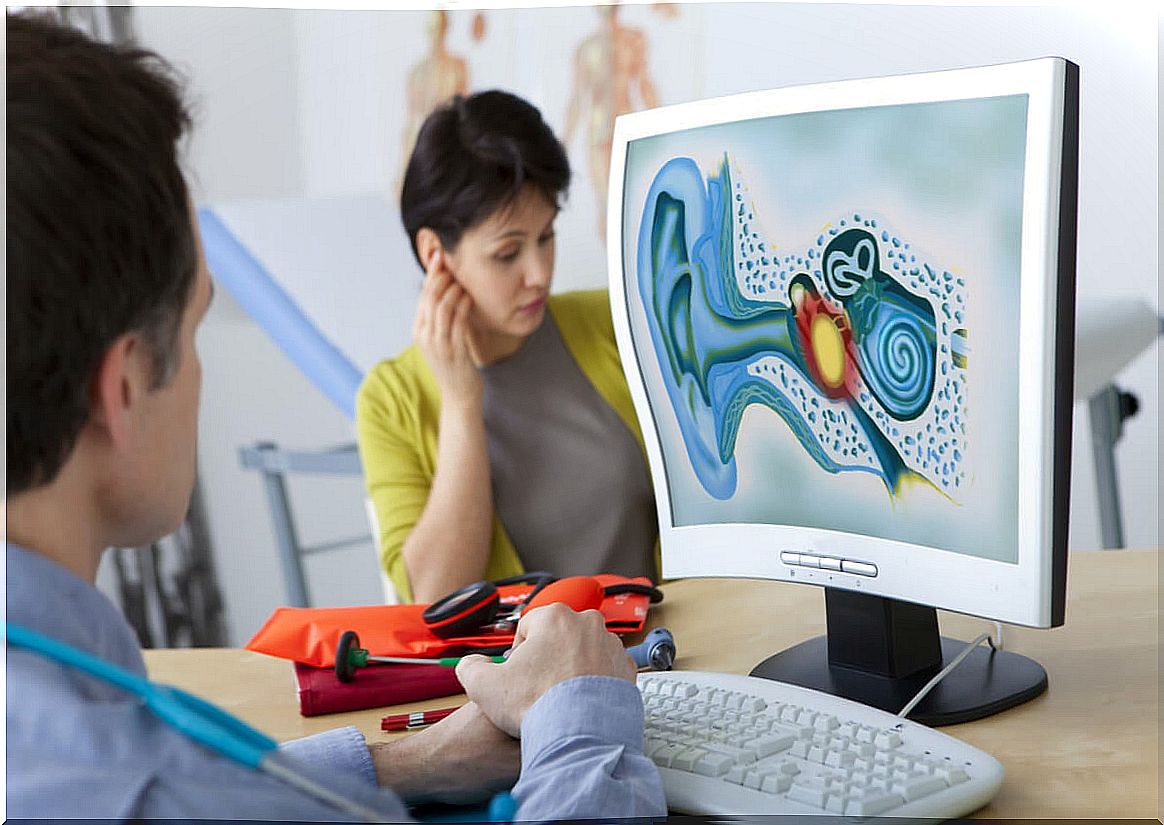

The diagnosis is made based on a clinical interview. This will inquire about the type of noise to which a person has been exposed. Also, you need a test called audiometry.
In this test, the patient is exposed to sounds of varying intensity and frequency. In this way, it is possible to evaluate if their perception is adequate or to what extent it is not. From this, a diagnosis is made.
Typically, treatment for acoustic trauma includes one or more of the following measures:
- Hearing protection. It consists of the use of special devices to reduce the perception of noise, when working or living in an environment with very intense sounds. They can be earplugs, protective hearing aids or others.
- Medications. When the acoustic trauma is temporary or acute, the doctor may prescribe oral steroids. The goal is to regain hearing function.
- Hearing assistance. It is the use of a device to compensate for hearing loss. The most common is a hearing aid. Nowadays, it is also common for a cochlear implant to be carried out, which is an advanced form of this type of device.
Prevention is the way
If the acoustic trauma is very severe, surgery may be necessary to reconstruct the eardrum. It should be noted that hearing loss can be treated, but not cured. Therefore, it is best to prevent ear injuries, particularly those caused by exposure to continuous noise.
Today, hearing aids of many kinds are available to compensate, in part, for hearing loss. They are usually comfortable, durable and are affordable for many people. The doctor will indicate which is the best option in each case.