What Is Selective Eating Syndrome?
Mostly suffered by children (and sometimes with parental approval), selective eating syndrome is based on not eating certain foods on a whim, or only eating a small number of ingredients.
This bad habit can lead to future problems, such as anorexia or bulimia. And, therefore, it must be supervised by a specialist. What is this disorder? We share its causes and the way to detect it in time.
What is selective eating disorder?
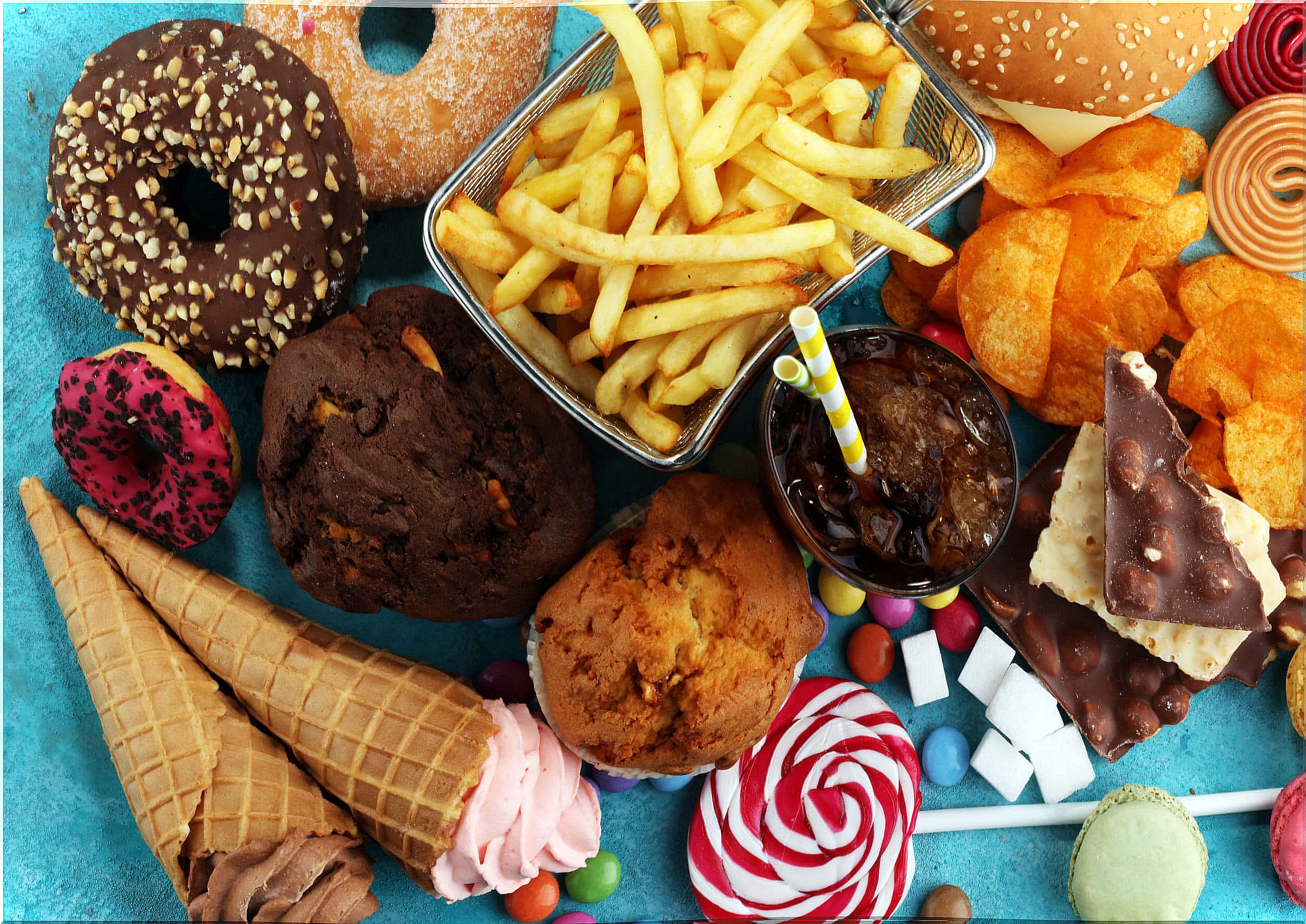

Do you know Selective Eating Disorder? It is a pathology that begins in childhood and that avoids or reduces the intake of some foods.
It begins as behavior accepted by the parents. It can even be instilled by them so as not to waste too much time cooking, or to let them choose their favorite foods. However, it can generate drawbacks in the development of children.
Related to whims or rudeness, selective eating syndrome leads children to eat only what they want; without accepting other types of foods “that they do not like”.
In most cases, the “approved” foods are hamburgers, French fries, pastries, and pizzas. The “not endorsed” ingredients are fruits and vegetables. The little ones eat junk food; and they don’t taste broccoli, apples, or lentils.
Serious consequences of this syndrome
Keep in mind that this disorder results in a nutritional deficiency. This happens by not meeting the vitamins, proteins and nutrients that the body needs.
The selective feeding syndrome can be “masked” in a supposed freedom of the child to eat what he likes. However, even if you do not want to consume fruits, you should do so for their sake and better development and growth.
Depending on what a person eats in childhood, so will his future. A child who is too “picky” when eating will perform poorly, get sick often, and be short.
A psychological problem
When talking about this disorder, it is related to a nutritional problem and a lack of nutrients. But unfortunately, it is also associated with some eating disorders, such as bulimia and anorexia because it is a syndrome that requires medical attention.
It is therefore necessary that children who refuse to eat certain foods, even if the parents insist, go to a consultation with a therapist. The help must be supported by the work of a nutritionist or pediatrician.
Children use this selection of food to express themselves or communicate. “Between the lines”, there is a grassroots problem that needs to be addressed.
Crying over a plate of chard, spitting up food if it contains carrots, or yelling at dinner are stressful behaviors for parents. As they do not want to see their children suffer, so they choose to cook only what they accept.
Although the attitude and intention of the parents are good, the truth is that they are hurting him more than you think. The problem will only grow, and before long, you will only be offered one or two menu options.
How to detect selective eating syndrome in my child?
It is more common in boys than in girls and, in addition to not wanting to eat certain foods, they have other symptoms:
- Anxiety problems.
- Social isolation.
- Obsessive and compulsive traits.
- Low adaptation to changes.
- Irritability and mood swings.
- Uncontrollable crying or screaming episodes.
- Nutritional deficiency and weight loss.
- Slowdown in development or growth.
What causes selective eating disorder?
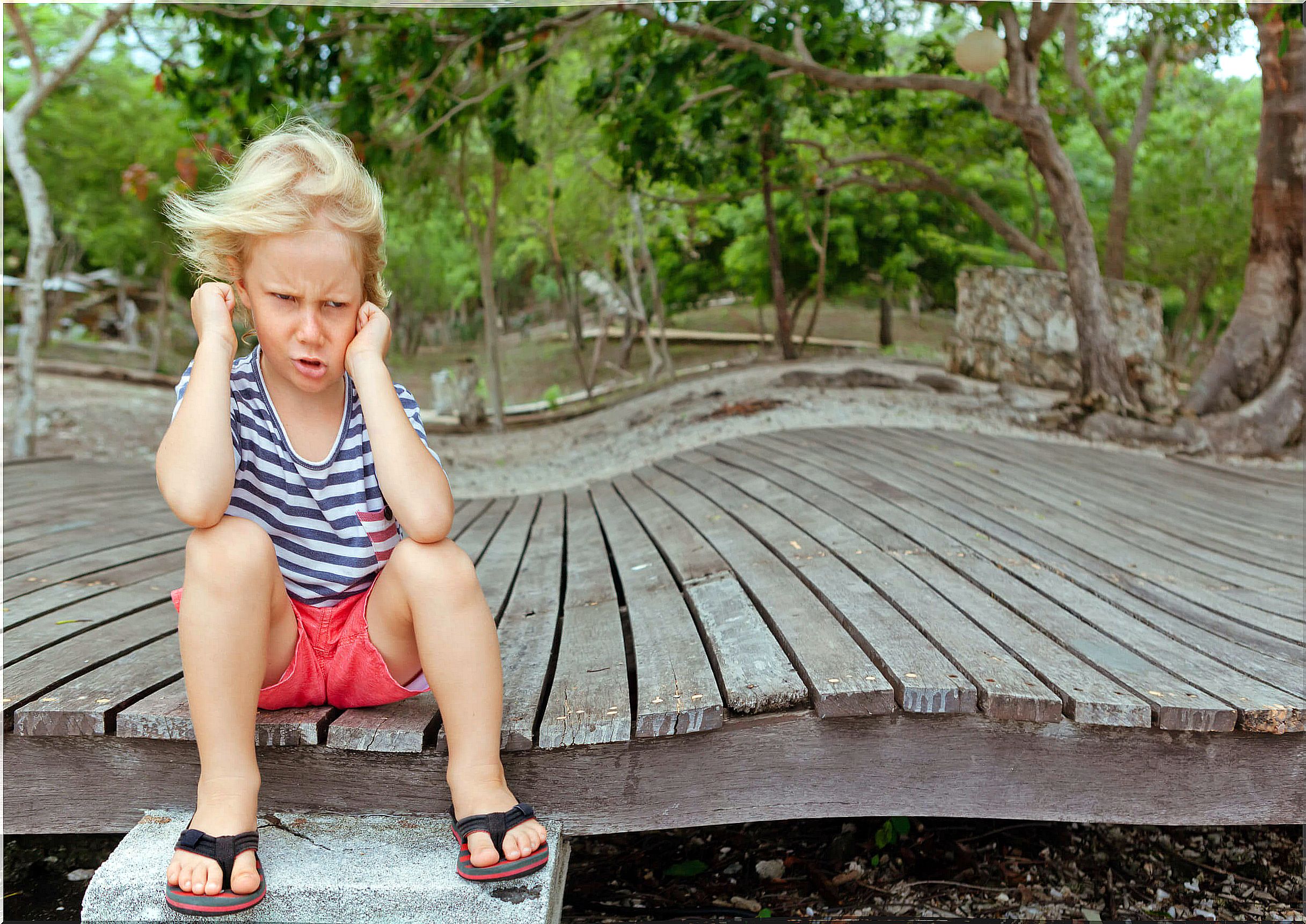

While there is no single trigger for this syndrome; Yes, it is related, for example, to problems with the parent-child bond. One way to express your discontent, to attract attention, or to ask for affection is to choose or cry over food.
Stress, traumatic situations or lack of care on the part of parents also trigger this problem. However, it can also be caused by overprotection : children who do not receive negatives and do what they want can suffer from this syndrome.
Do not put limits or rules on your children, compensate for a lack of dedication or time with “allowances” or gifts … These are other causes of selective eating.
How to prevent the syndrome?
To prevent “I don’t like”, “I don’t eat this,” or “I don’t want to” at dinner time, parents or caregivers need to be clever, smart, and patient enough. Faced with the first refusal, threats or phrases like “you eat it because I said so” are not worth much.
It is good to know that children imitate their parents and the adults around them. Therefore, if the mother, father or older brother selects the food on the plate or says that they do not like such food, they will reject the same foods.
The family diet must be made up of varied ingredients. In the event that, for example, one of the parents requires a different menu, involve the child or leave him out of the conversation.
Trying different recipes, making fun and colorful dishes, or encouraging them to help cook are great ways to teach your child to eat well. Offering fruits and vegetables from a young age and not always giving them carbohydrates, fats and sugars contributes to improving their health, achieving better development and avoiding eating disorders.